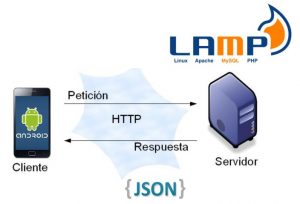
Enviar y recibir datos en JSON con Retrofit
Uso de Retrofit para realizar peticiones GET, POST, PUT y DELETE
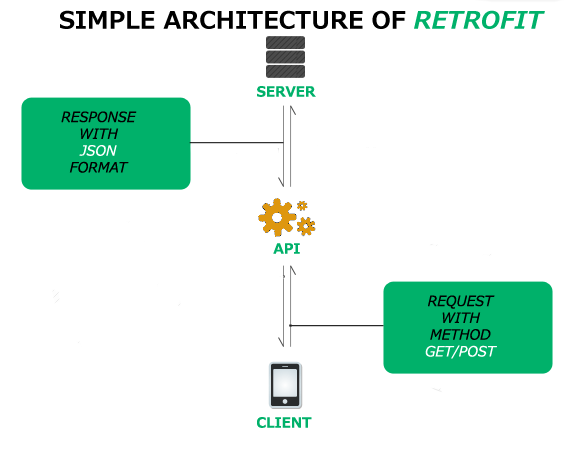
Cómo consumir una API y procesar la respuesta usando Retrofit
| Annotation | Description |
|---|---|
@Path |
variable substitution for the API endpoint (i.e. username will be swapped for {username} in the URL endpoint). |
@Query |
specifies the query key name with the value of the annotated parameter. |
@Body |
payload for the POST call (serialized from a Java object to a JSON string) |
@Header |
specifies the header with the value of the annotated parameter |
Ejercicio con Retrofit: Repositorios en Kotlin
Tutorial de Retrofit 2 avanzado en Kotlin
/**
* Created by aristidesguimeraorozco on 29/4/18.
*/
interface APIService {
@GET
fun getCharacterByName(@Url url: String): Call<DogsResponse>
@GET("/example/example2/{id}/loquesea")
fun getCharacterByName2(@Path("id") id: String): Call<DogsResponse>
@GET("/example/example2/v2/loquesea")
fun getCharacterByName3(
@Query("pet") pet: String,
@Query("name") name: String
): Call<DogsResponse>
@POST
fun getEVERYTHING(@Body exampleArisDto: ExampleArisDto): Call<*>
@Multipart
@POST
fun getEVERYTHING2(
@Part image: MultipartBody.Part,
@Part("example") myExample: String
): Call<*>
// val requestBody = RequestBody.create(MediaType.parse(getContentResolver().getType(fileUri)), file);
// val a = MultipartBody.Part.createFormData("picture", file.getName(), requestBody);
}
data class ExampleArisDto(val name: String, val age: Int)
Más información:
Deja una respuesta
Lo siento, debes estar conectado para publicar un comentario.